Inspiolto® Respimat®
This product is manufactured by Boehringer Ingelheim and is a combination of two ingredients, tiotropium bromide monohydrate and olodaterol hydrochloride.
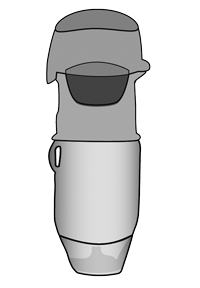
This product is inhaled into the lungs using the Respimat®.
play
Respimat®
Why is it prescribed?
- Inspiolto® Respimat® is a combination long-acting muscarinic antagonist (LAMA) and a long-acting beta2-agonist (LABA) indicated for the long term maintenance bronchodilator treatment of COPD, including chronic bronchitis and emphysema.
- Each box contains 1 Respimat® inhaler and 1 cartridge, providing 60 puffs (30 medicinal doses). Physician samples provide 28 puffs (14 medicinal doses).
- The color of the cap of the Respimat® inhaler is color coded to match the cartridge.
- Never spray the medication toward the eyes
- Before the inhaler is used for the first time, the cartridge must be inserted into the inhaler and then primed.
- Prepare For First Time Use:
- Step 1. With the green cap closed, press the safety catch while pulling off the clear base. Be careful not to touch the piercing element located inside thebottom of the clear base.
- Step 2. Write the discard by date on the label of the inhaler. The discard by date is 3 months from the date the cartridge is inserted into the inhaler.
- Step 3. Take the cartridge out of the box. Push the narrow end of the cartridge into the inhaler. The base of the cartridge will not sit flush with the inhaler. About 1/8 of an inch will remain visible when the cartridge is correctly inserted. The cartridge can be pushed against a firm surface to ensure that it is correctly inserted. Do not remove the cartridge once it has been inserted into the inhaler.
- Step 4. Put the clear base back into place. Do not remove the clear base again. The inhaler should not be taken apart after you have inserted the cartridge and put the clear base back.
- Prime For First Time Use:
- The following steps are needed to fill the dosing system the first time you use it and will not affect the number of doses available. After preparation and initial priming, the inhaler will be able to deliver the labeled number of doses (30 or 14). Proper priming of the inhaler is important to make sure the correct amount of medicine is delivered.
- Step 5. Hold the inhaler upright, with the green cap closed, to avoid accidental release of the dose. Turn the clear base in the direction of the black arrows on the label until it clicks (half a turn).
- Step 6. Flip the green cap until it snaps fully open.
- Step 7. Point the inhaler toward the ground (away from your face). Press the dose release button. Close the green cap. Repeat Steps 5, 6, and 7 until a spray is visible. Once the spray is visible, you must repeat Steps 5, 6, and 7 three more times to make sure the inhaler is prepared for use. The inhaler is now ready to use. These steps will not affect the number of doses available. After preparation and initial priming, the inhaler will be able to deliver the labeled number of doses (30 or 14).
- Daily Dosing:
- Step A. Hold the inhaler upright with the green cap closed, so you do not accidentally release a dose of medicine. Turn the clear base in the direction of the black arrows on the label until it clicks (half a turn).
- Step B. Flip the green cap until it snaps fully open. Breathe out slowly and fully, and then close your lips around the end of the mouthpiece without covering the air vents. Point the inhaler to the back of your throat. While taking in a slow, deep breath through your mouth, press the dose release button and continue to breathe in slowly for as long as you can. Hold your breath for 10 seconds or for as long as comfortable. Repeat Step A and Step B so that you get the full dose. Close the green cap until you use the inhaler again.
- Helpful Hints for Daily Dosing: If the inhaler has not been used for more than 3 days, spray 1 puff toward the ground to prepare the inhaler for use. If it has not been used for more than 21 days, repeat Steps 5, 6, and 7 until a spray is visible. Then repeat Steps 5, 6, and 7 three more times to prepare the inhaler for use.
- The dose indicator shows approximately how much medicine is left. When the pointer enters the red area of the scale, there is enough medicine for 7 days (30 dose product) or 3 days (14 dose product). This is when you need to refill your prescription.
- Once the dose indicator has reached the end of the scale, all puffs have been used and the inhaler locks automatically. At this point, the base cannot be turned any further.
- Throw away the Inspiolto® Respimat® inhaler 3 months after insertion of cartridge into inhaler, even if all the medicine has not been used, or when the inhaler is locked, whichever comes first.
- Store at room temperature.
Alternatives
See other products used in the treatment of •bronchospasm associated with COPD •chronic bronchitis (COPD) •COPD •emphysema (COPD) •bronchitis •
Adults 18 years of age and older: The recommended dose of Inspiolto® Respimat® is 2 puffs (5 mcg tiotropium and 5 mcg olodaterol), once daily at the same time of the day, every day.
- Inspiolto® Respimat® contains two active ingredients: tiotropium, a long-acting muscarinic antagonist (LAMA), and olodaterol, a long-acting beta2-adrenergic agonist (LABA).
- Tiotropium and olodaterol relax the muscles in the walls of the small airways in the lungs. Both of these medicines work together to help open the airways and make it easier for air to get in and out of the lungs. When taken as prescribed, tiotropium and olodaterol help keep the airways open, which can prevent shortness of breath.
Side effects may include:
- increase of the measured eye pressure
- seeing halos around lights or colored images in association with red eyes
- blurred vision
- diarrhea
- constipation
- dry mouth
- inflammation of the mouth, gums and tongue
- difficulty in swallowing
- heartburn
- feeling tired
- general weakness
- inflammation of the throat, nasal passages and sinuses
- common cold
- fungal infections of the oral cavity and throat
- depletion of body water
- back pain
- swollen and painful joints
- muscular pain
- muscle spasms
- feeling dizzy difficulty sleeping cough
- pain in mouth and throat
- hoarseness
- nosebleed
- sore throat and discomfort when swallowing
- inflammation/irritation of the vocal cords
- pain when passsing urine
- inability to empty the bladder
- rash
- itching
- nettle rash
- infections or ulcerations of the skin
- dryness of the skin
If any of these affects you severely, tell your doctor, or pharmacist.
- BEFORE you use Inspiolto® Respimat® talk to your doctor, nurse, or pharmacist if you:
- have heart problems, such as rapid or irregular heart beat or abnormal electrical signal called "prolongation of th QT interval"
- have high blood pressure
- have seizures
- have thyroid problems
- have diabetes
- have been told you react strongly to sympathomimetic amines (a class of drugs that includes LABA drugs) or if you are allergic to ipratropium bromide or other drugs which are anticholinergic (contrain atropine or its derivatives)
- have any other medical problems such as difficulty with urination or enlarged prostate
- have eye problems, such as glaucoma, or eye pain
- have any allergies to food or drugs
- have kidney disease
- are pregnant or planning to become pregnant. It is not known if Inspiolto® Respimat® can harm your unborn baby
- are breastfeeding. It is not known if Inspiolto® Respimat® passes into your milk and if it can harm your baby.
As with most medicines, interactions with other drugs are possible. Tell your doctor or pharmacist about all the medicines you are taking. The following may interact with Inspiolto®:
- antidepressants, in particular tricyclic antidepressants and monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs);
- similar medications used for your lung disease as it may increase the risk of experiencing possible side effects;
- medicines that decrease the level of potassium in your blood. These include diuretics (also known as “water pills” and are used to treat high blood pressure e.g. hydrochlorothiazide), other bronchodilators such as methylxanthines (e.g. theophylline) or steroids (e.g. prednisolone);
- beta-blockers used in the treatment of high blood pressure or other heart problems (e.g. propranolol) or in the treatment of glaucoma (e.g. timolol).
